Publications
Publications by categories in reversed chronological order.
2026
-
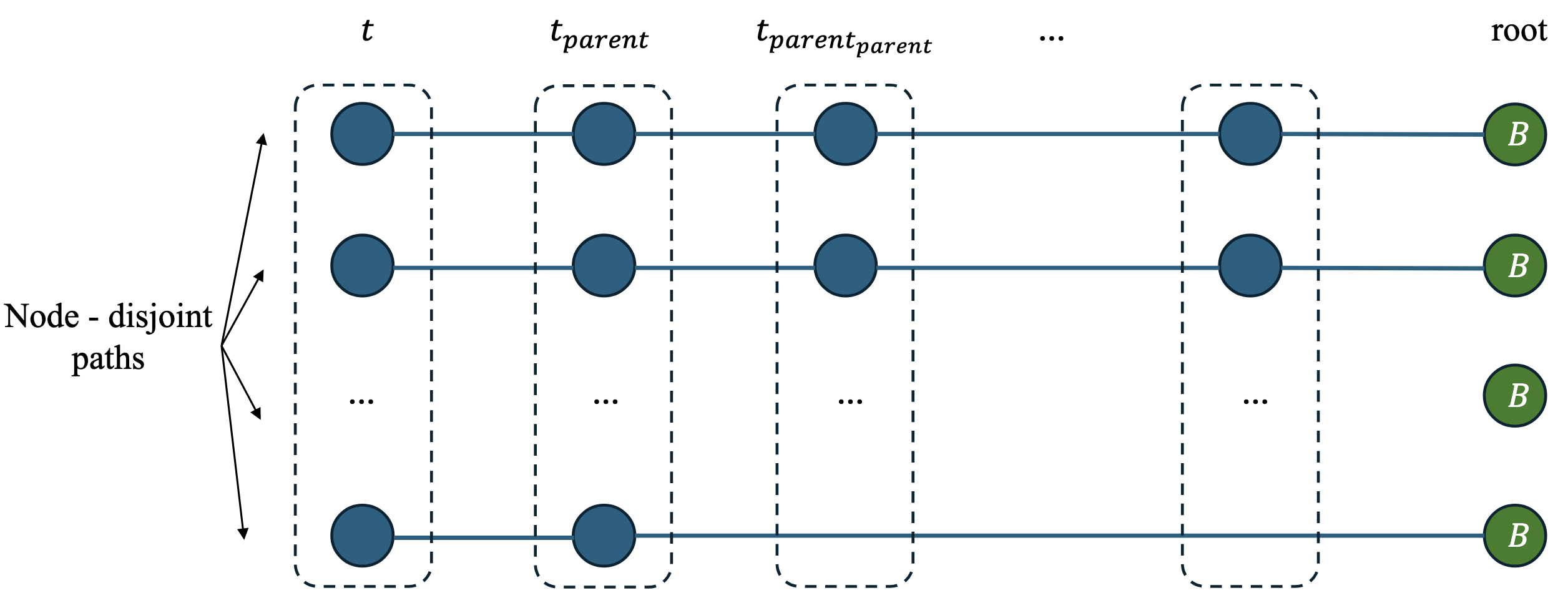 STEAM: Securing the connections in wireless sensor networks with varying target priorityTruong Q. Vu, Minh T. Trinh, Hien Q. Ta, and 2 more authorsComputer Networks, 2026
STEAM: Securing the connections in wireless sensor networks with varying target priorityTruong Q. Vu, Minh T. Trinh, Hien Q. Ta, and 2 more authorsComputer Networks, 2026Achieving multi-connections in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) has been drawing attention from the research community. This paper addresses the problem of providing secure and reliable multi-connectivity in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) when different targets require different connectivity priorities and security levels. Existing multi-connectivity approaches do not incorporate secured communication constraints, operate only in simplified 2D settings, or employ high-complexity algorithms. We formalize the Q-Secure Connectivity problem, which extends Q-Connectivity by enforcing target-dependent secure communication ranges to prevent eavesdropping. To solve this problem efficiently, we propose Sensor Tree Establishment and Adjacency Mapping (STEAM), a novel graph-based heuristic that minimizes the number of relay nodes while ensuring node-disjoint and secure paths. STEAM builds a minimum spanning tree over targets and applies a Hungarian-based mapping to construct feasible connections. Experiments on realistic 3D datasets show that STEAM significantly reduces relay-node count by 3 times and computation time by 15 times, and achieves 30% lower energy consumption, 20% lower outage probability, 40% lower latency, and 50% higher throughput compared to the state-of-the-art method. This work provides the first practical solution to Q-Secure Connectivity in realistic 3D environments.
2025
-
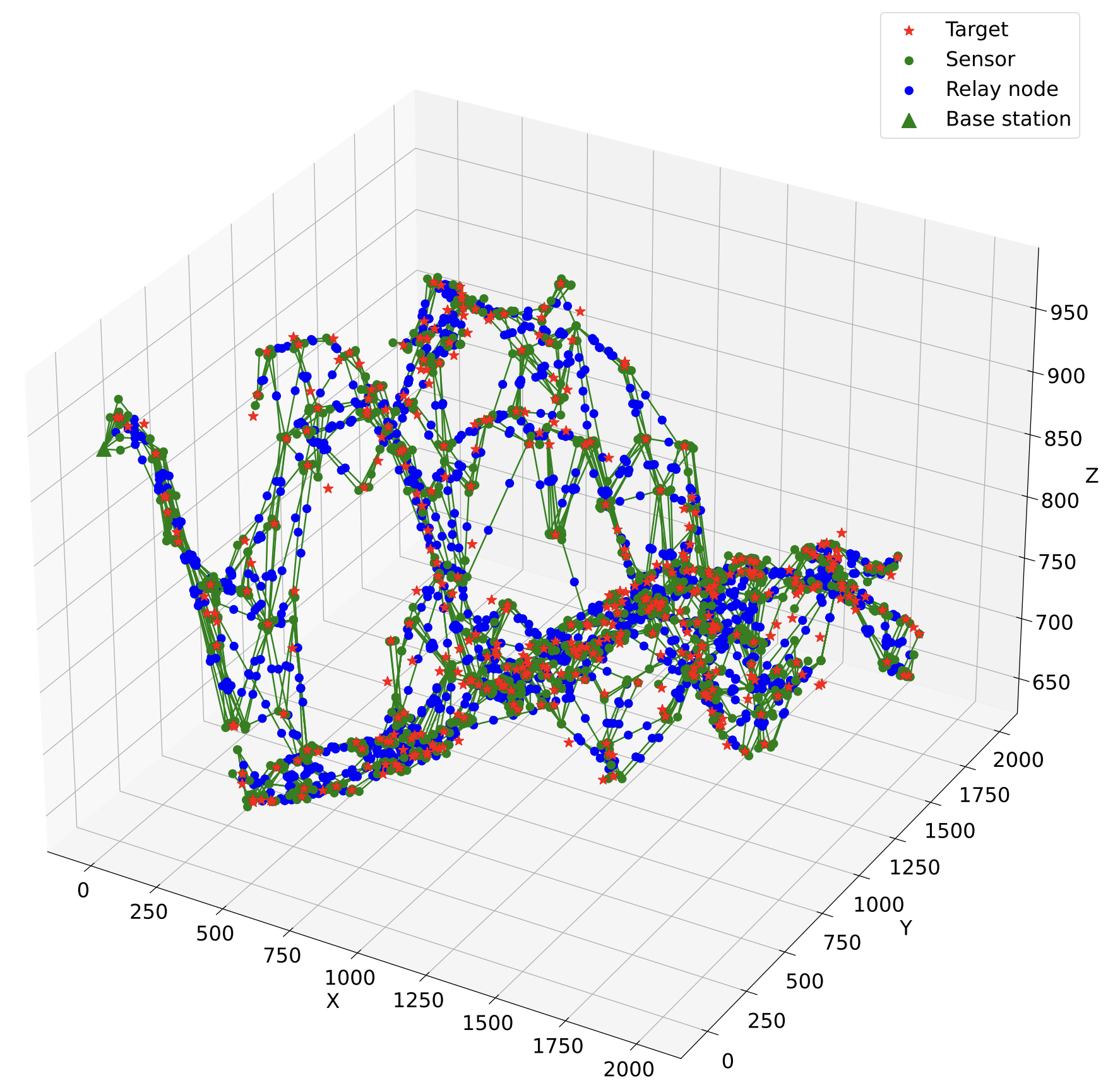 SPARTA-GEMSTONE: A two-phase approach for efficient node placement in 3D WSNs under Q-Coverage and Q-Connectivity constraintsQuang Truong Vu, The Minh Trinh, Thi Hanh Nguyen, and 4 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, 2025
SPARTA-GEMSTONE: A two-phase approach for efficient node placement in 3D WSNs under Q-Coverage and Q-Connectivity constraintsQuang Truong Vu, The Minh Trinh, Thi Hanh Nguyen, and 4 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, 2025Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) face challenges in achieving robust target coverage and connectivity, particularly when varying priorities for targets are modeled with Q-Coverage and Q-Connectivity constraints. However, existing studies often neglect minimizing the number of nodes under these constraints in 3D environments or focus on sensor-to-sensor connections, which are less suitable for target-oriented networks. This paper bridges these gaps by proposing a novel two-phase heuristic approach. In Phase I, we introduce SPARTA, with two variants (SPARTA-CC and SPARTA-CP), to address Q-Coverage. Phase II employs GEMSTONE, a heuristic algorithm based on a minimum spanning tree, to ensure Q-Connectivity. Our method is evaluated on a real-world 3D dataset and compared against baseline methods. The results demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces the number of nodes while improving running speed. Our proposal can save 13% of the node count while running 2370 times faster than the current state-of-the-art method. These contributions advance the state of the art in WSN design and hold significant implications for efficient and fault-tolerant network deployment in practical scenarios.
-
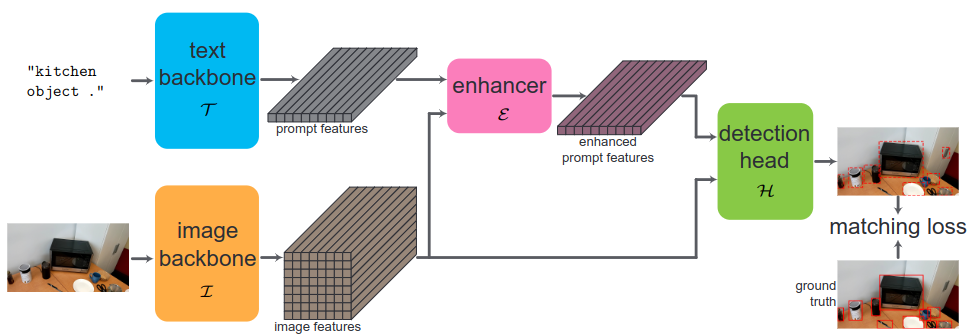 Low-Rank Prompt Adaptation for Open-Vocabulary Object DetectionZekun Zhang*, Vu Quang Truong*, and Minh HoaiIn ICCV 2025 Workshop, 2025
Low-Rank Prompt Adaptation for Open-Vocabulary Object DetectionZekun Zhang*, Vu Quang Truong*, and Minh HoaiIn ICCV 2025 Workshop, 2025Open-vocabulary object detectors (OVDs) have emerged as versatile tools for detecting various objects in diverse, real-world scenarios, thanks to their ability to recognize objects based on any input textual prompt. However, selecting the optimal prompts for specific objects of interest can be challenging, often requiring a laborious and suboptimal trial-and-error process. This paper focuses on Grounding DINO, a well-known OVD, and proposes a data-driven approach featuring an annotation- and parameter-efficient framework for prompt optimization. Specifically, we introduce a lightweight low-rank prompt enhancement module for adaptation. This module learns to enrich the features of an initial prompt with attention to the image feature, guiding the detector to better identify objects of interest using a limited number of images and a tiny number of parameters. Our method is efficient and achieves significant precision improvements. Experiments with Grounding DINO on several object detection datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach compared to other recent state-of-the-art parameter-efficient tuning methods. Furthermore, we apply our adapted OVD to the Unseen Object Instance Segmentation (UOIS) task, showing that high-quality box prompts from our optimized detector, when fed into Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2), are sufficient to achieve state-of-the-art performance with only a few box-annotated training images. Code and trained models are at https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/PromptAdaptOVD.
2024
-
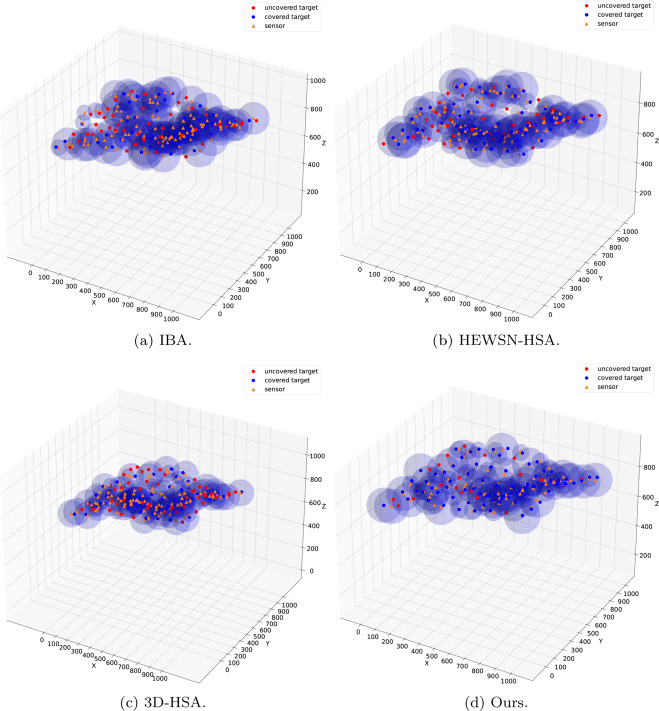 Striking the perfect balance: Multi-objective optimization for minimizing deployment cost and maximizing coverage with Harmony SearchQuang Truong Vu, Phuc Tan Nguyen, Thi Hanh Nguyen, and 3 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, 2024
Striking the perfect balance: Multi-objective optimization for minimizing deployment cost and maximizing coverage with Harmony SearchQuang Truong Vu, Phuc Tan Nguyen, Thi Hanh Nguyen, and 3 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, 2024In the Internet of Things (IoT) era, wireless sensor networks play a critical role in communication systems. One of the most crucial problems in wireless sensor networks is the sensor deployment problem, which attempts to provide a strategy to place the sensors within the surveillance area so that two fundamental criteria of wireless sensor networks, coverage and connectivity, are guaranteed. In this paper, we look to solve the multi-objective deployment problem so that area coverage is maximized and the number of nodes used is minimized. Since Harmony Search is a simple yet suitable algorithm for our work, we propose Harmony Search algorithm along with various enhancement proposals, including heuristic initialization, random sampling of sensor types, weighted fitness evaluation, and using different components in the fitness function, to provide a solution to the problem of sensor deployment in a heterogeneous wireless sensor network where sensors have different sensing ranges. On top of that, the probabilistic sensing model is used to reflect how the sensors work realistically. We also provide the extension of our solution to 3D areas and propose a realistic 3D dataset to evaluate it. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithms solve the area coverage problem more efficiently than previous algorithms. Our best proposal demonstrates significant improvements in coverage ratio by 10.20% and cost saving by 27.65% compared to the best baseline in a large-scale evaluation.
-
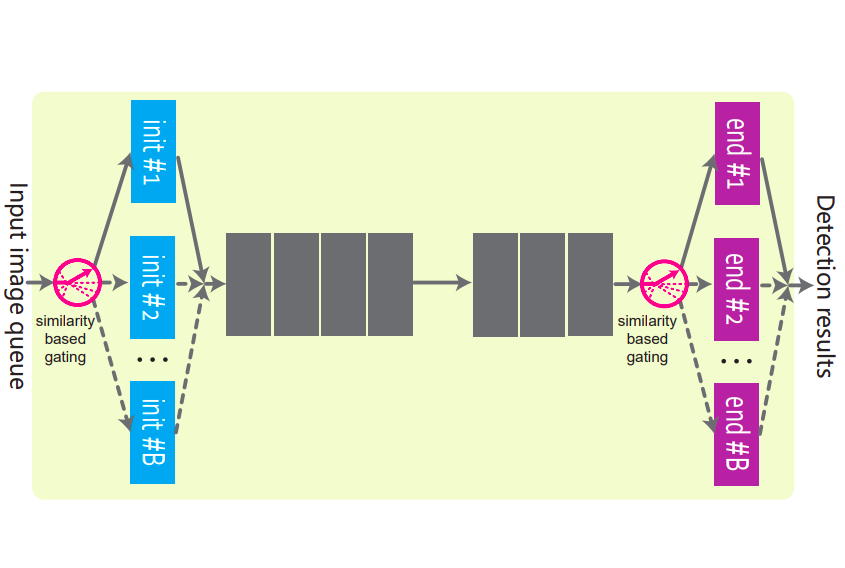 Efficiency-preserving Scene-adaptive Object DetectionZekun Zhang, Vu Quang Truong, and Minh HoaiIn Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, 2024
Efficiency-preserving Scene-adaptive Object DetectionZekun Zhang, Vu Quang Truong, and Minh HoaiIn Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, 2024We present a framework that enables an object detector to self-enhance its accuracy while preserving its efficiency. This framework is particularly useful in settings where a single object detector is deployed to detect objects in video streams from numerous cameras. Our approach improves the object detector’s precision by adapting it to specific scenes in a novel way that does not hinder the inference speed or overall system throughput. Specifically, it involves augmenting the object detector with a mixture-of-experts structure that only moderately increases the parameter count, avoiding the expense of replicating the entire model. The resulting enhanced detector operates as a self-contained unit, facilitating an efficient client-server architecture with a shared detection engine for multiple video streams. Our framework supports self-supervised learning, eliminating the reliance on manually annotated data, and it is compatible with various established object detector architectures. Experiments on the Scenes100 dataset demonstrate the wide applicability and effectiveness of our method in enhancing detection precision while maintaining operational efficiency. Our code is available at https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/scenes100/tree/main/moe.
2023
-
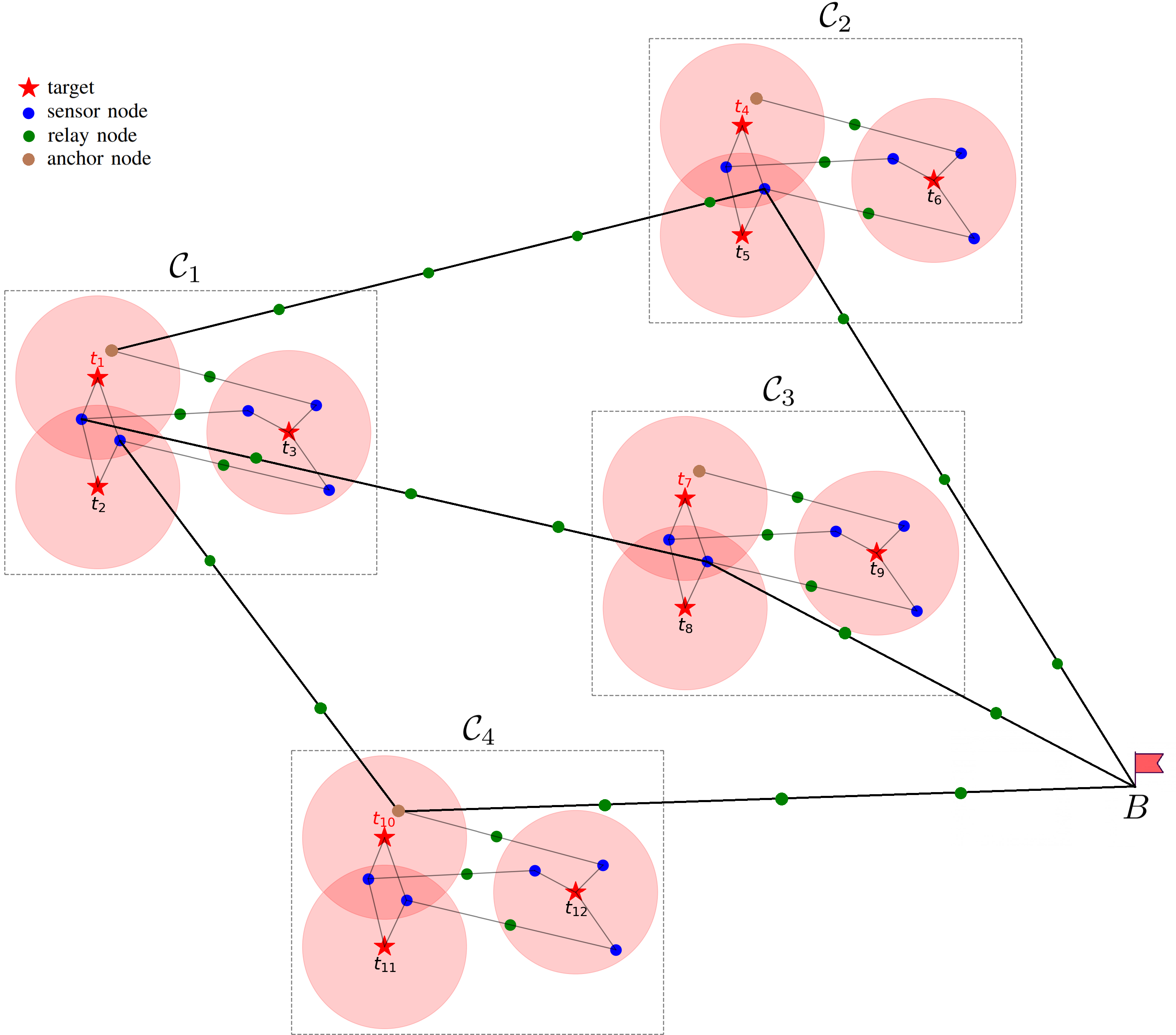 Node placement optimization under Q-Coverage and Q-Connectivity constraints in wireless sensor networksNguyen Thi Hanh, Huynh Thi Thanh Binh, Vu Quang Truong, and 2 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, 2023
Node placement optimization under Q-Coverage and Q-Connectivity constraints in wireless sensor networksNguyen Thi Hanh, Huynh Thi Thanh Binh, Vu Quang Truong, and 2 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, 2023Target coverage and connectivity problems are major challenges for wireless sensor networks (WSNs). In practice, when different targets demand different priority levels, each target is assigned a value q which is the number of sensors covering it as well as the number of node-disjoint paths to transfer sensing data of itself to the base station. When q>1, the network can ensure fault tolerance. Those constraints are named Q-Coverage and Q-Connectivity. In this paper, we propose a two-phase solution for the problem: Greedy combined with Linear Programming (GLA) for Phase I and Clustering combined with graph Max Flow Approach (CMFA) for Phase II. Besides, we also evaluate the algorithms with multiple datasets and make some comparisons with baseline methods (ESSNP in phase I; CCMFA and FCSA in phase II). Our results show that the proposed algorithms significantly improve in various evaluation metrics compared to baseline methods. Furthermore, the results can be advantageous for our future researches on WSNs in general and target coverage in particular.